Division B
Acceptable Solutions
Part 9 — Housing and Small Buildings
Section 9.4. Structural Requirements
9.4.1. Structural Design Requirements and Application Limitations
9.4.1.1. General
(See Appendix A.)1)  Subject to the application limitations defined elsewhere in this Part, structural members and their connections shall
Subject to the application limitations defined elsewhere in this Part, structural members and their connections shall
 Subject to the application limitations defined elsewhere in this Part, structural members and their connections shall
Subject to the application limitations defined elsewhere in this Part, structural members and their connections shalla) conform to requirements provided elsewhere in this Part,
b) be designed according to good engineering practice such as that
provided in CWC 2009, “Engineering Guide for Wood Frame Construction,” or
2)  Where floor framing is designed in accordance with Clause (1)(b) or (c), and where supporting wall framing and fastenings, or footings, are designed according to Clause (1)(a), the specified live load on the floor shall not exceed 2.4 kPa.
Where floor framing is designed in accordance with Clause (1)(b) or (c), and where supporting wall framing and fastenings, or footings, are designed according to Clause (1)(a), the specified live load on the floor shall not exceed 2.4 kPa.
 Where floor framing is designed in accordance with Clause (1)(b) or (c), and where supporting wall framing and fastenings, or footings, are designed according to Clause (1)(a), the specified live load on the floor shall not exceed 2.4 kPa.
Where floor framing is designed in accordance with Clause (1)(b) or (c), and where supporting wall framing and fastenings, or footings, are designed according to Clause (1)(a), the specified live load on the floor shall not exceed 2.4 kPa. 3)  Location-specific information for structural design, including snow and wind loads and seismic spectral response accelerations, shall
be determined according to Subsection 1.1.3.
Location-specific information for structural design, including snow and wind loads and seismic spectral response accelerations, shall
be determined according to Subsection 1.1.3.
 Location-specific information for structural design, including snow and wind loads and seismic spectral response accelerations, shall
be determined according to Subsection 1.1.3.
Location-specific information for structural design, including snow and wind loads and seismic spectral response accelerations, shall
be determined according to Subsection 1.1.3.9.4.2. Specified Loads
9.4.2.1. Application
1) This Subsection applies to light-frame constructions whose wall, floor and roof planes
are generally comprised of frames of small repetitive structural members, and where
a) the roof and wall planes are clad, sheathed or braced on at least one side,
b) the small repetitive structural members are spaced not more than 600 mm o.c.,
c) the clear span of any structural member does not exceed 12.2 m,
d) the maximum deflection of the structural roof members conforms to Article 9.4.3.1.,
e) the maximum total roof area, notwithstanding any separation of adjoining buildings by firewalls, is 4 550 m2, and
f) for flat roofs, there are no significant obstructions on the roof, such as parapet
walls, spaced closer than the distance calculated by
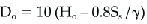 where
where
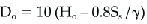
Do= minimum distance between obstructions, m,
Ho= height of the obstruction above the roof, m,
Ss= ground snow load, kPa, and
ϒ= unit weight of snow, kN/m3.

9.4.2.2. Specified Snow Loads
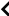 (See Appendix A.)
(See Appendix A.)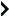
1)  Except as provided in Sentences (2) and (3), specified snow loads shall be not less than those calculated using the following formula:
Except as provided in Sentences (2) and (3), specified snow loads shall be not less than those calculated using the following formula:
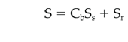 where
where
 Except as provided in Sentences (2) and (3), specified snow loads shall be not less than those calculated using the following formula:
Except as provided in Sentences (2) and (3), specified snow loads shall be not less than those calculated using the following formula:
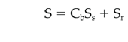
S= specified snow load,
Cb= basic snow load roof factor, which is 0.45 where the entire width
of the roof does not exceed 4.3 m and 0.55 for all other
roofs,
Ss= 1-in-50-year ground snow load in kPa, determined according to
Subsection 1.1.3., and
Sr= associated 1-in-50-year rain load in kPa, determined according to
Subsection 1.1.3.
3)  Bow string, arch or semi-circular roof trusses having an unsupported span greater than 6 m shall be designed in conformance
with the snow load requirements in Subsection 4.1.6.
Bow string, arch or semi-circular roof trusses having an unsupported span greater than 6 m shall be designed in conformance
with the snow load requirements in Subsection 4.1.6.
 Bow string, arch or semi-circular roof trusses having an unsupported span greater than 6 m shall be designed in conformance
with the snow load requirements in Subsection 4.1.6.
Bow string, arch or semi-circular roof trusses having an unsupported span greater than 6 m shall be designed in conformance
with the snow load requirements in Subsection 4.1.6.
9.4.2.3. Platforms Subject to Snow and Occupancy Loads
1)  Balconies, decks and other accessible exterior platforms intended for an occupancy and subject to snow loads shall be designed to carry the specified roof snow load or 1.9
kPa, whichever is greater, where the platform, or each segregated
area of the platform, serves a single dwelling unit. (See Appendix A.)
Balconies, decks and other accessible exterior platforms intended for an occupancy and subject to snow loads shall be designed to carry the specified roof snow load or 1.9
kPa, whichever is greater, where the platform, or each segregated
area of the platform, serves a single dwelling unit. (See Appendix A.)
 Balconies, decks and other accessible exterior platforms intended for an occupancy and subject to snow loads shall be designed to carry the specified roof snow load or 1.9
kPa, whichever is greater, where the platform, or each segregated
area of the platform, serves a single dwelling unit. (See Appendix A.)
Balconies, decks and other accessible exterior platforms intended for an occupancy and subject to snow loads shall be designed to carry the specified roof snow load or 1.9
kPa, whichever is greater, where the platform, or each segregated
area of the platform, serves a single dwelling unit. (See Appendix A.) 9.4.2.4. Attics and Roof Spaces
1)  The ceiling joists or truss bottom chords in residential attic or roof spaces having limited accessibility that precludes the storage of equipment or material shall be designed
for a total specified load of not less than 0.35 kPa,
where the total specified load is the sum of the specified dead load plus the specified live load of the ceiling. (See Appendix A.)
The ceiling joists or truss bottom chords in residential attic or roof spaces having limited accessibility that precludes the storage of equipment or material shall be designed
for a total specified load of not less than 0.35 kPa,
where the total specified load is the sum of the specified dead load plus the specified live load of the ceiling. (See Appendix A.)
 The ceiling joists or truss bottom chords in residential attic or roof spaces having limited accessibility that precludes the storage of equipment or material shall be designed
for a total specified load of not less than 0.35 kPa,
where the total specified load is the sum of the specified dead load plus the specified live load of the ceiling. (See Appendix A.)
The ceiling joists or truss bottom chords in residential attic or roof spaces having limited accessibility that precludes the storage of equipment or material shall be designed
for a total specified load of not less than 0.35 kPa,
where the total specified load is the sum of the specified dead load plus the specified live load of the ceiling. (See Appendix A.) 9.4.3. Deflections
9.4.3.1. Deflections
1)  The maximum deflection of structural members shall conform to Table 9.4.3.1.
The maximum deflection of structural members shall conform to Table 9.4.3.1.
 The maximum deflection of structural members shall conform to Table 9.4.3.1.
The maximum deflection of structural members shall conform to Table 9.4.3.1.| Table 9.4.3.1. Maximum Deflections Forming part of Sentence 9.4.3.1.(1) | ||
| Structural Members | Type of Ceiling Supported | Max. Allowable Deflection as an Expressed Ratio of the Clear Span |
| Roof rafters, roof joists and roof beams | No ceiling | 1/180 |
| Other than plaster or gypsum board | 1/240 | |
| Plaster or gypsum board | 1/360 | |
| Ceiling joists | Other than plaster or gypsum board | 1/240 |
| Plaster or gypsum board | 1/360 | |
| Floor beams, floor joists and floor decking | All cases | 1/360 |
|
Beams, joists and decking for balconies, decks and other accessible exterior platforms |
Serving a single dwelling unit |
1/240 |
|
Other |
1/360 |
|
9.4.4. Foundation Conditions
9.4.4.1. Allowable Bearing Pressures
1)  Footing sizes for shallow foundations shall be
Footing sizes for shallow foundations shall be
 Footing sizes for shallow foundations shall be
Footing sizes for shallow foundations shall bea) determined in accordance with Section 9.15.,
or
b) designed in accordance with Section 4.2. using
i) the maximum allowable bearing pressures in Table 9.4.4.1., or
ii) allowable bearing pressures determined from subsurface investigation.
| Table 9.4.4.1. Allowable Bearing Pressure for Soil or Rock Forming part of Sentence 9.4.4.1.(1) | |
| Maximum Allowable Bearing Pressure, kPa | |
|
Dense or compact sand or gravel(1) |
150 |
|
Loose sand or gravel(1) |
50 |
|
Dense or compact silt(1) |
100 |
|
Stiff clay(1) |
150 |
|
Firm clay(1) |
75 |
|
Soft clay(1) |
40 |
| Till | 200 |
| Clay shale | 300 |
|
Sound rock |
500 |
| Notes to Table 9.4.4.1.: | |
|
|
|
| (1) | See Appendix A. |
9.4.4.2. Foundation Capacity in Weaker Soil and Rock
1)  Where a soil or rock within a distance equal to twice the footing width below the bearing surface has a lower allowable bearing pressure than that at the bearing surface as shown in Article 9.4.4.1., the design capacity of the foundation shall not be greater than would cause the weakest soil or rock to be stressed beyond its allowable bearing pressure.
Where a soil or rock within a distance equal to twice the footing width below the bearing surface has a lower allowable bearing pressure than that at the bearing surface as shown in Article 9.4.4.1., the design capacity of the foundation shall not be greater than would cause the weakest soil or rock to be stressed beyond its allowable bearing pressure.
 Where a soil or rock within a distance equal to twice the footing width below the bearing surface has a lower allowable bearing pressure than that at the bearing surface as shown in Article 9.4.4.1., the design capacity of the foundation shall not be greater than would cause the weakest soil or rock to be stressed beyond its allowable bearing pressure.
Where a soil or rock within a distance equal to twice the footing width below the bearing surface has a lower allowable bearing pressure than that at the bearing surface as shown in Article 9.4.4.1., the design capacity of the foundation shall not be greater than would cause the weakest soil or rock to be stressed beyond its allowable bearing pressure. 2)  In calculating subsurface pressures referred to in Sentence (1), the loads from the footings shall be assumed to be distributed uniformly over a horizontal plane within
a frustum extending downward from the footing at an angle of 60° to the horizontal.
In calculating subsurface pressures referred to in Sentence (1), the loads from the footings shall be assumed to be distributed uniformly over a horizontal plane within
a frustum extending downward from the footing at an angle of 60° to the horizontal.
 In calculating subsurface pressures referred to in Sentence (1), the loads from the footings shall be assumed to be distributed uniformly over a horizontal plane within
a frustum extending downward from the footing at an angle of 60° to the horizontal.
In calculating subsurface pressures referred to in Sentence (1), the loads from the footings shall be assumed to be distributed uniformly over a horizontal plane within
a frustum extending downward from the footing at an angle of 60° to the horizontal.
9.4.4.3. High Water Table
1)  Where a foundation bears on gravel, sand or silt, and the water table is within a distance below the bearing surface equal to the width of the foundation, the allowable bearing pressure shall be 50% of that determined in Article 9.4.4.1.
Where a foundation bears on gravel, sand or silt, and the water table is within a distance below the bearing surface equal to the width of the foundation, the allowable bearing pressure shall be 50% of that determined in Article 9.4.4.1.
 Where a foundation bears on gravel, sand or silt, and the water table is within a distance below the bearing surface equal to the width of the foundation, the allowable bearing pressure shall be 50% of that determined in Article 9.4.4.1.
Where a foundation bears on gravel, sand or silt, and the water table is within a distance below the bearing surface equal to the width of the foundation, the allowable bearing pressure shall be 50% of that determined in Article 9.4.4.1.9.4.4.4. Soil Movement
1)  Where a foundation is located in an area where soil movement caused by changes in soil moisture content, freezing, or chemical-microbiological oxidation is known to occur to the extent that it will damage a building, measures shall be taken to preclude such movement or to reduce its effects on the building so that the building's stability and the performance of assemblies will not be adversely
affected. (See Appendix A.)
Where a foundation is located in an area where soil movement caused by changes in soil moisture content, freezing, or chemical-microbiological oxidation is known to occur to the extent that it will damage a building, measures shall be taken to preclude such movement or to reduce its effects on the building so that the building's stability and the performance of assemblies will not be adversely
affected. (See Appendix A.)
 Where a foundation is located in an area where soil movement caused by changes in soil moisture content, freezing, or chemical-microbiological oxidation is known to occur to the extent that it will damage a building, measures shall be taken to preclude such movement or to reduce its effects on the building so that the building's stability and the performance of assemblies will not be adversely
affected. (See Appendix A.)
Where a foundation is located in an area where soil movement caused by changes in soil moisture content, freezing, or chemical-microbiological oxidation is known to occur to the extent that it will damage a building, measures shall be taken to preclude such movement or to reduce its effects on the building so that the building's stability and the performance of assemblies will not be adversely
affected. (See Appendix A.) 2) The potential for slope instability and its consequences, such as slope
displacement, shall be evaluated based on site-specific material properties and
ground motion parameters referenced in Subsection 1.1.3. and shall be taken into
account in the design of the structure and its foundations.
9.4.4.5. Retaining Walls
9.4.4.6. Walls Supporting Drained Earth
(See A-9.4.4.6. and 9.15.1.1. in Appendix A.)1)  Except where constructed in accordance with Section 9.15., walls supporting drained earth shall be designed
Except where constructed in accordance with Section 9.15., walls supporting drained earth shall be designed
 Except where constructed in accordance with Section 9.15., walls supporting drained earth shall be designed
Except where constructed in accordance with Section 9.15., walls supporting drained earth shall be designeda) for a pressure equivalent to that exerted by a fluid that has
a density of not less than 480 kg/m3 and
a depth equal to that of the retained earth, or
b) in accordance with Section 4.2. so as to be
able to resist the loads and effects described in Article 4.1.2.1.
2)  Walls supporting other than drained earth shall be designed
Walls supporting other than drained earth shall be designed
 Walls supporting other than drained earth shall be designed
Walls supporting other than drained earth shall be designeda) for the pressure described in Clause (1)(a) plus the fluid pressure of the surcharge, or
b) in accordance with Section 4.2. so as to be
able to resist the loads and effects described in Article 4.1.2.1.
